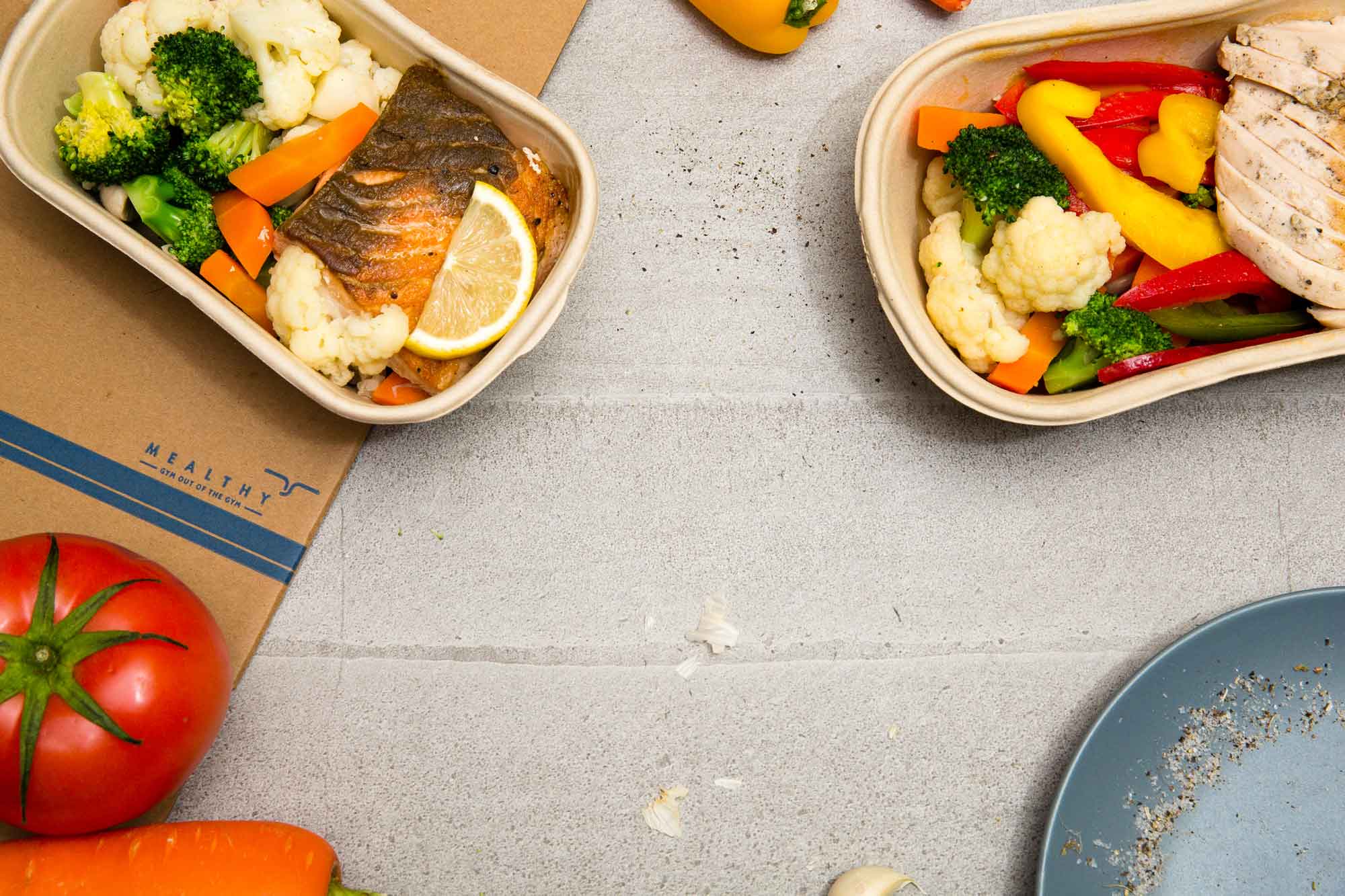

Getting started
How it works
-

Pick your meals
A new menu of nutritionist designed options every week.
-

Chef-made
Delicious meals perfectly cooked by our talented chefs
-
Heat and Eat
No prep. No mess. Meals arrive ready to heat and eat in 3 minutes.
This Week's Low-Carb Menu
Fuel Your Body with Nourishing Low-Carb Meals
-
Calories 480kcl Protein 41g Carbs 13g Fat 30g
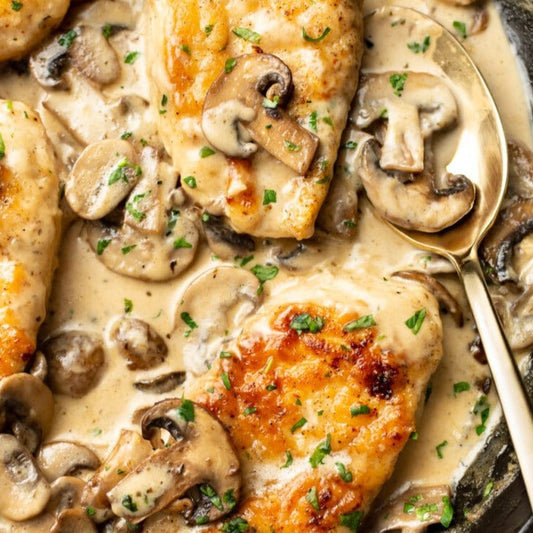

Baked Chicken and Mushrooms (Keto)
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per -
Calories 550kcl Protein 35g Carbs 23g Fat 38g
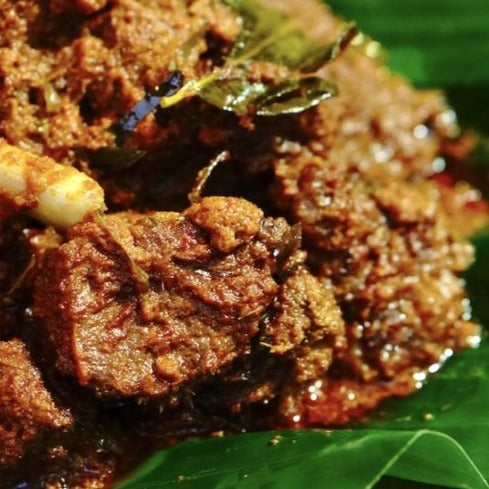

Beef Rendang (low carb)
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per -
Calories 470kcl Protein 71g Carbs 9g Fat 14g
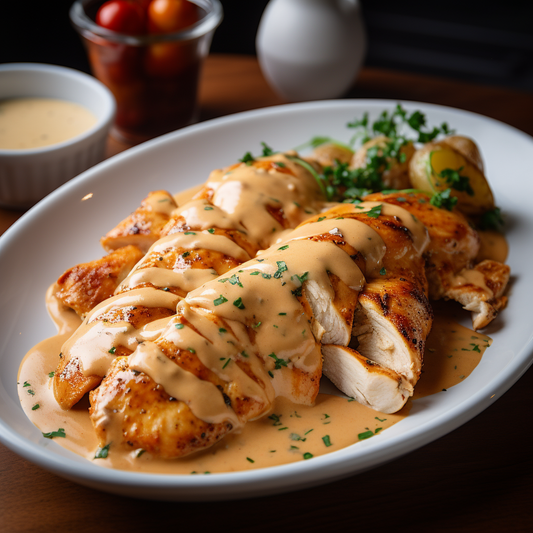

Chicken Protein+
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per -
Calories 570kcl Protein 41g Carbs 47g Fat 24g
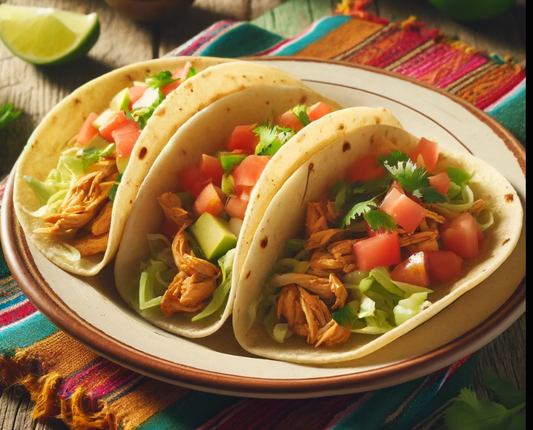

Chicken Tacos
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per -
Calories 450kcl Protein 39g Carbs 13g Fat 27g
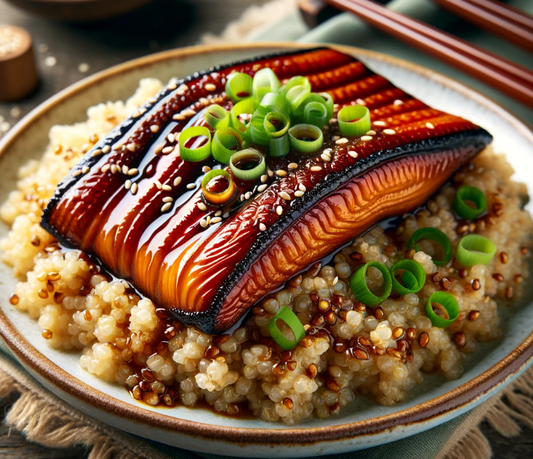

Grilled Eel (Low-carb)
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per -
Calories 450kcl Protein 40g Carbs 15g Fat 26g
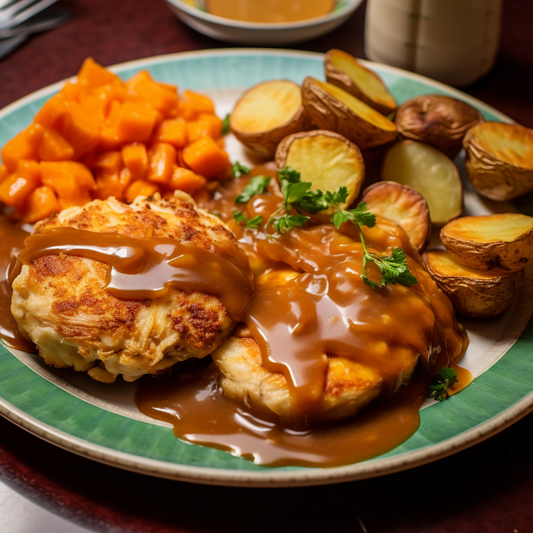

Homemade Chicken Patties (Low-Carb)
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per -
Calories 360kcl Protein 30g Carbs 19g Fat 18g
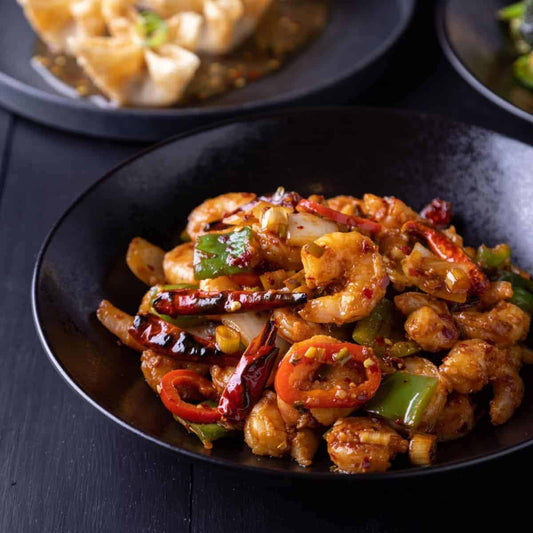

Kungpao Prawns (Keto)
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per -
Calories 360kcl Protein 40g Carbs 21g Fat 13g
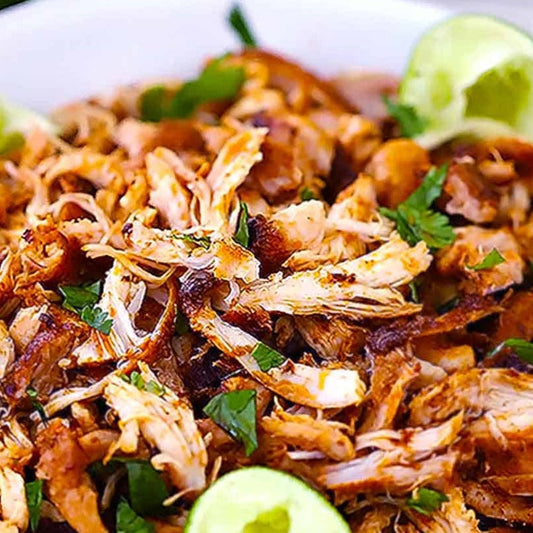

Mexican Shredded Chicken (Keto)
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per
Fresh, Healthy & Delicious
-

Fresh Meals
Clean meals made to order.
-

Chef-Made
Cooked to perfection by our skilled chefs. Taste the difference.
-

Get Results
Meals designed to get you real results.
As seen in
-

"Mealthy is on a mission to provide the ultimate solution to food-prep flexibility..."
-

"A range of healthy pre-packed meals by Mealthy"
-

"Mealthy’s plans are laser-targeted at helping you achieve fat loss or muscle gain goals..."
-

"Mealthy Food is a result-oriented meal prep service that aims to help you build muscle and lose fat through its meal plans. "
-

"making Mealthy perfect for those who are conscious about nutrition"
-

"their chefs will select the premium and seasonal ingredients, with accurate portion controls"
Chef's Choice
Nourishing and Delicious Healthy Meals
-
Calories 520kcl Protein 43g Carbs 27g Fat 27g
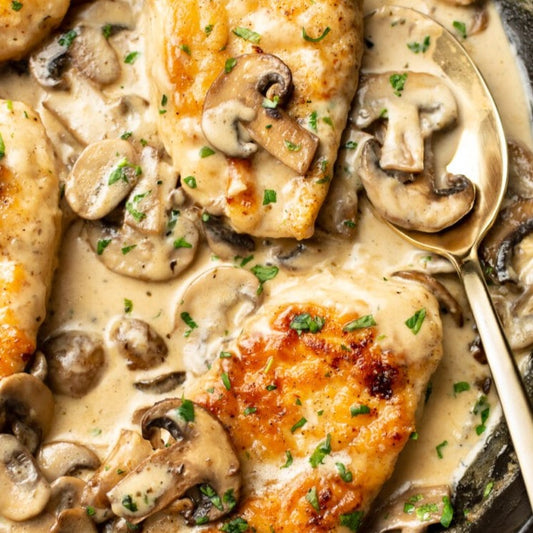

Baked Chicken and Mushrooms
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per -
Calories 630kcl Protein 36g Carbs 39g Fat 38g
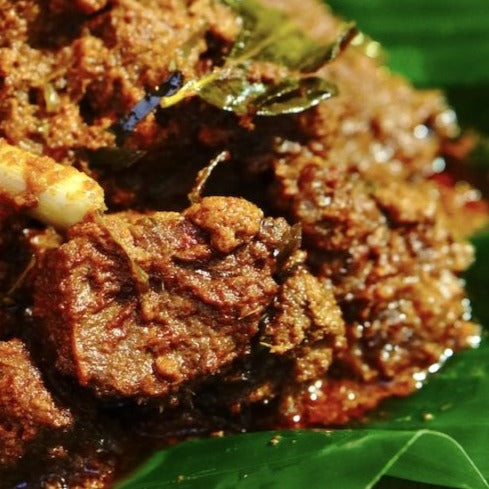

Beef Rendang
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per -
Calories 470kcl Protein 71g Carbs 9g Fat 14g

Chicken Protein+
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per -
Calories 570kcl Protein 41g Carbs 47g Fat 24g

Chicken Tacos
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per -
Calories 520kcl Protein 40g Carbs 28g Fat 27g
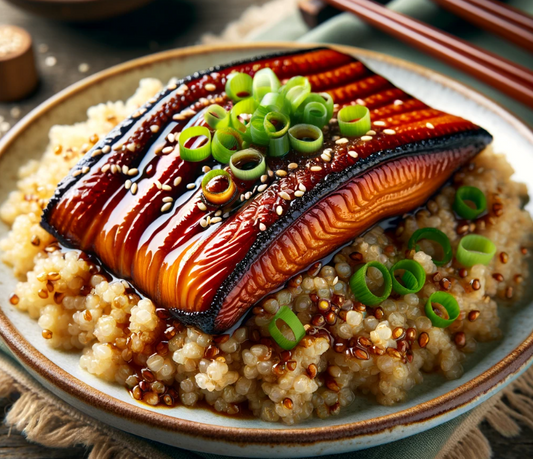

Grilled Eel
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per -
Calories 500kcl Protein 40g Carbs 27g Fat 26g
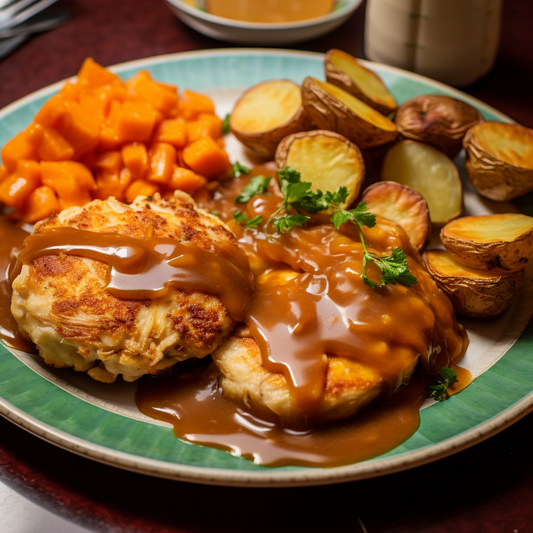

Homemade Chicken Patties
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per -
Calories 460kcl Protein 32g Carbs 39g Fat 20g
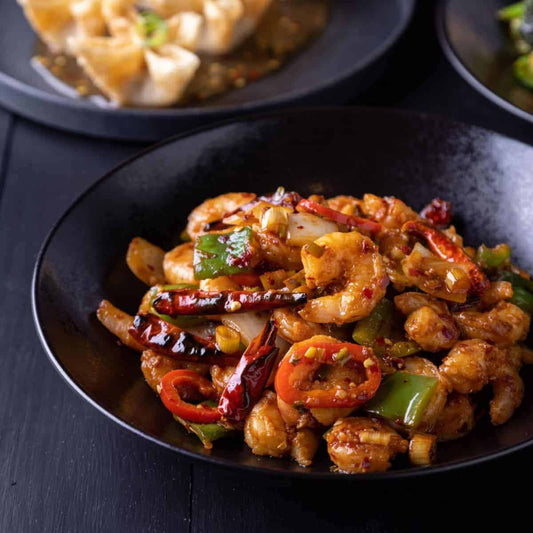

Kungpao Prawns
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per -
Calories 450kcl Protein 40g Carbs 40g Fat 14g
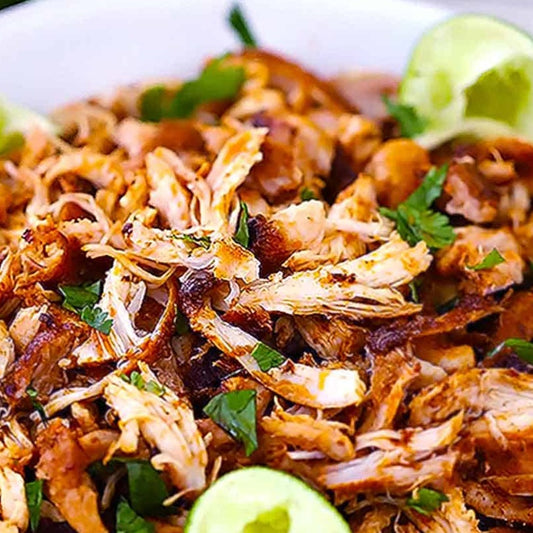

Mexican Shredded Chicken
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per -
Calories 360kcl Protein 40g Carbs 19g Fat 14g
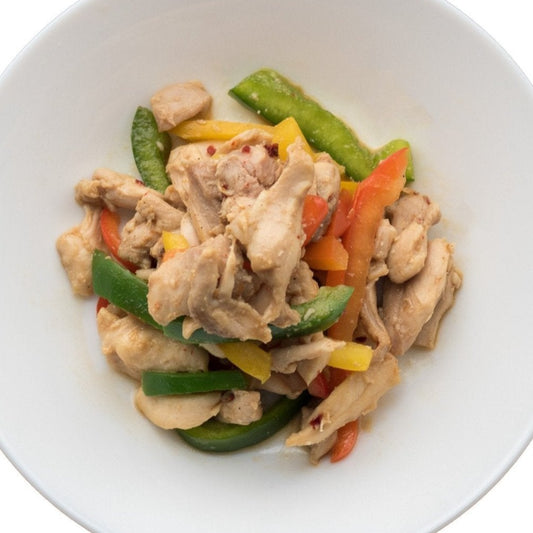

Peppers & Chicken
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per -
Calories 480kcl Protein 46g Carbs 25g Fat 21g

Pork Chop with Spring Onion
Regular price $150Regular priceUnit price / per

Ready-made Meals Starting at HK$89 per Meal
Get fully-prepared, fresh meals delivered to your doorstep. No commitment necessary — skip or cancel at any time.
Skip or cancel any time
What our customers say
-
Delicious, simple, and great service! /Carmen
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
-
I tried it. Good taste, good meal & good for workout. /Stefan
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
-
Thanks Mealthy for the amazing healthy meals delivered to my home!! /Sienna
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
-
Love the meals and the results. /Michelle
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
-
good meal! GOOD! /Ryan
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
-
Much much better than expected. /Ahmad
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
Blog posts
View all-

How Mealthy Works: Personalized Meal Delivery f...
Mealthy is a meal delivery service that aims to provide a personalized and sustainable approach to healthy eating. With our diverse menu choices, including the Chef's Choice and Low-Carb/Keto options,...
How Mealthy Works: Personalized Meal Delivery f...
Mealthy is a meal delivery service that aims to provide a personalized and sustainable approach to healthy eating. With our diverse menu choices, including the Chef's Choice and Low-Carb/Keto options,...
-

Starting a Low Carb or Keto Diet: A Guide for M...
If you're considering embarking on a low carb or keto diet, you've come to the right place. These diets have gained popularity for their health benefits, including weight loss and...
Starting a Low Carb or Keto Diet: A Guide for M...
If you're considering embarking on a low carb or keto diet, you've come to the right place. These diets have gained popularity for their health benefits, including weight loss and...
-

The Importance of Staying Hydrated: Tips for Ke...
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining optimal health and well-being, especially in a bustling city like Hong Kong. With its hot and humid climate, it's essential to prioritize hydration to...
The Importance of Staying Hydrated: Tips for Ke...
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining optimal health and well-being, especially in a bustling city like Hong Kong. With its hot and humid climate, it's essential to prioritize hydration to...
-

Meal Prepping 101: How Mealthy Can Help You Sav...
In today's fast-paced world, finding time to prepare healthy meals can be a challenge. That's where meal prepping comes in. Meal prepping involves planning and preparing meals in advance, allowing...
Meal Prepping 101: How Mealthy Can Help You Sav...
In today's fast-paced world, finding time to prepare healthy meals can be a challenge. That's where meal prepping comes in. Meal prepping involves planning and preparing meals in advance, allowing...
































